MQTT and CoAP both are the most popular Internet of Things protocols. During the next post, we will talk about pros and cons of each one.
What is MQTT?
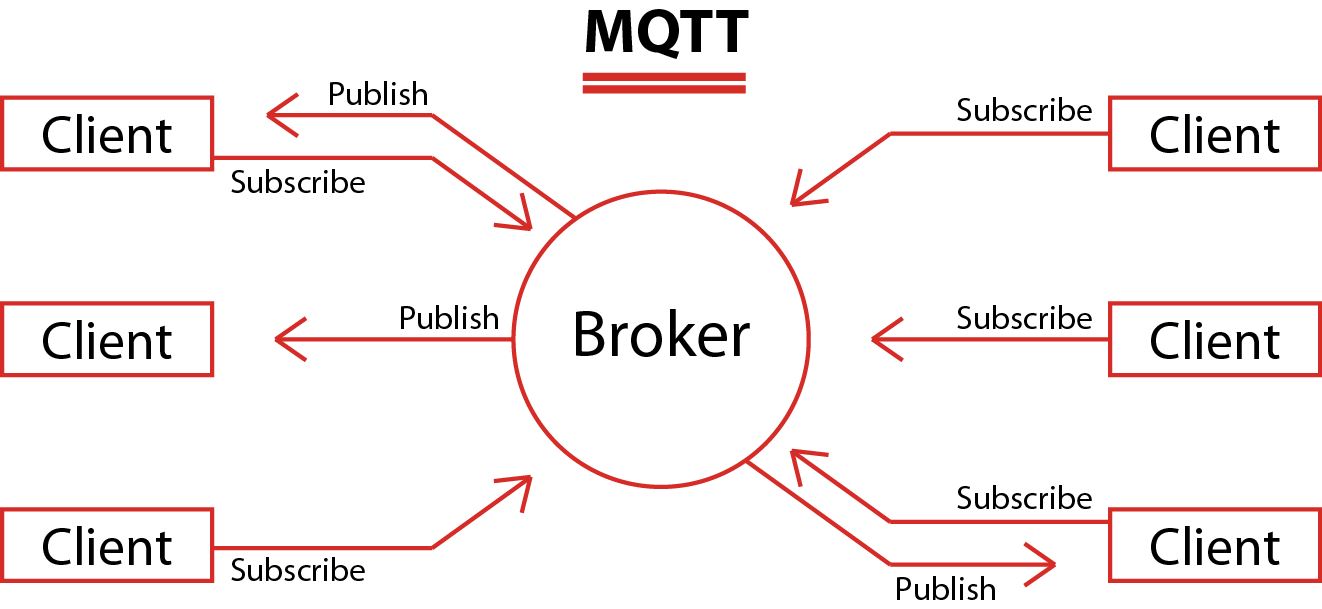
Message Queue Telemetry Transport (MQTT), is a publish-subscribe protocol that facilitates one-to-many communication mediated by brokers. Clients can publish messages to a broker and/or subscribe to a broker to receive certain messages. Messages are organized by topics, which essentially are “labels” that act as a system for dispatching messages to subscribers.
What is CoAP?
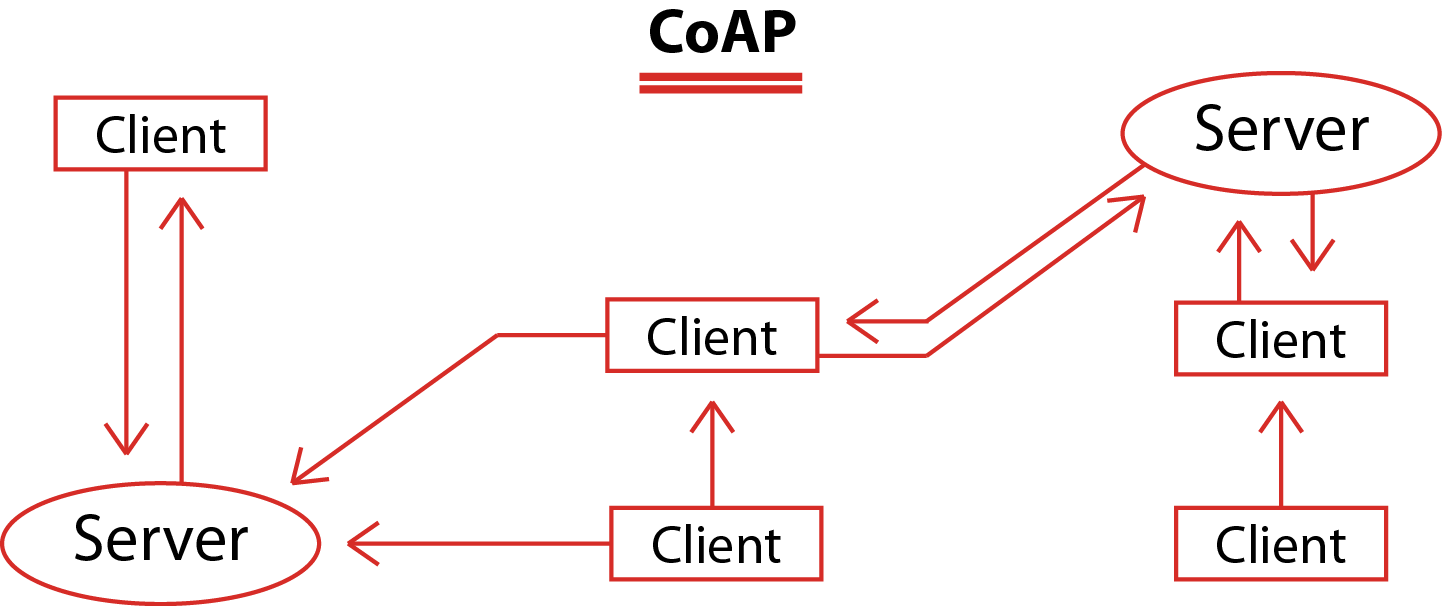
Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP), is a client-server protocol that, unlike MQTT, is not yet standardized. With CoAP, a client node can command another node by sending a CoAP packet. The CoAP server will interpret it, extract the payload, and decide what to do depending on its logic. The server does not necessarily have to acknowledge the request.
The following table compares different features and shows the strengths and debilities of each protocol:
| Features | MQTT | CoAP |
|---|---|---|
|
Base protocol |
TCP | UDP |
|
Model used for communication |
Publish-Subscribe |
Request-Response |
|
Communication node |
M:N | 1:1 |
|
Power consumption |
Higher than CoAP | Lower than MQTT |
|
RESTful |
No | Yes |
|
Number of messages type used |
16 | 4 |
|
Header size |
2 Bytes | 4 Bytes |
|
Messaging |
Asynchronous | Asynchronous & Synchronous |
|
Reliability |
3 Quality of service levels QoS 0: Delivery not guaranteed QoS 1: Delivery confirmation QoS 2: Delivery double confirmation |
Confirmable messages Non-confirmable messages Aknowledgements Retransmissions |
|
Implementation |
Easy to implement Hard to add extensions |
Few existing libraries and support |
|
Security |
Not defined Can use TLS/SSL |
DTLS or IPSec |
|
Other |
Useful for connections with remote location No error-handling |
Low overhead Low latency NAT issues |
Other IoT protocols
There are other protocols that can be used for IoT applications like AMQP, XMPP, DDS or LwM2M. In fact, what is really important is the knowledge of one’s own business needs and requirements, awareness of the advantages and drawbacks of the protocols offered by the market, and the ability to pick the one that best suits a given use case.
If you are interested in learning more about topics related to Internet of Things, Big Data, Industry 4.0 and Analytics, do not hesitate to continue reading our publications in the News section.
Also, don’t forget to follow us on Twitter , Linkedin and other social networks to be permanently updated.